Leading Film Faced Plywood Manufacturing
Leading Film Faced Plywood Manufacturing

If you’re planning to build a house or any structure that requires support beams, you’ll need to make sure you choose the right type of wood beam. Structural wood beams are an essential component of any building project. They provide the necessary support and stability needed to ensure the structure is safe and secure.
There are different types of structural wood beams, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most popular types include finger-jointed wood beams, glulam wood beams, and LVL (laminated veneer lumber) beams. Finger-jointed wood beams are made from many short pieces of solid wood joined together. They are constructed longitudinally and connected by finger joints. Glulam wood beams are made by gluing together several layers of wood to create a strong, durable beam. LVL beams are made by bonding thin wood veneers together to create a strong, stable beam.
Choosing the right type of structural wood beam for your project will depend on several factors, including the span of the beam, the load it will bear, and the aesthetic you’re trying to achieve. It’s important to work with a professional builder or engineer to determine the best type of beam for your specific project. With the right type of structural wood beam, you can ensure your building project is strong, stable, and safe.

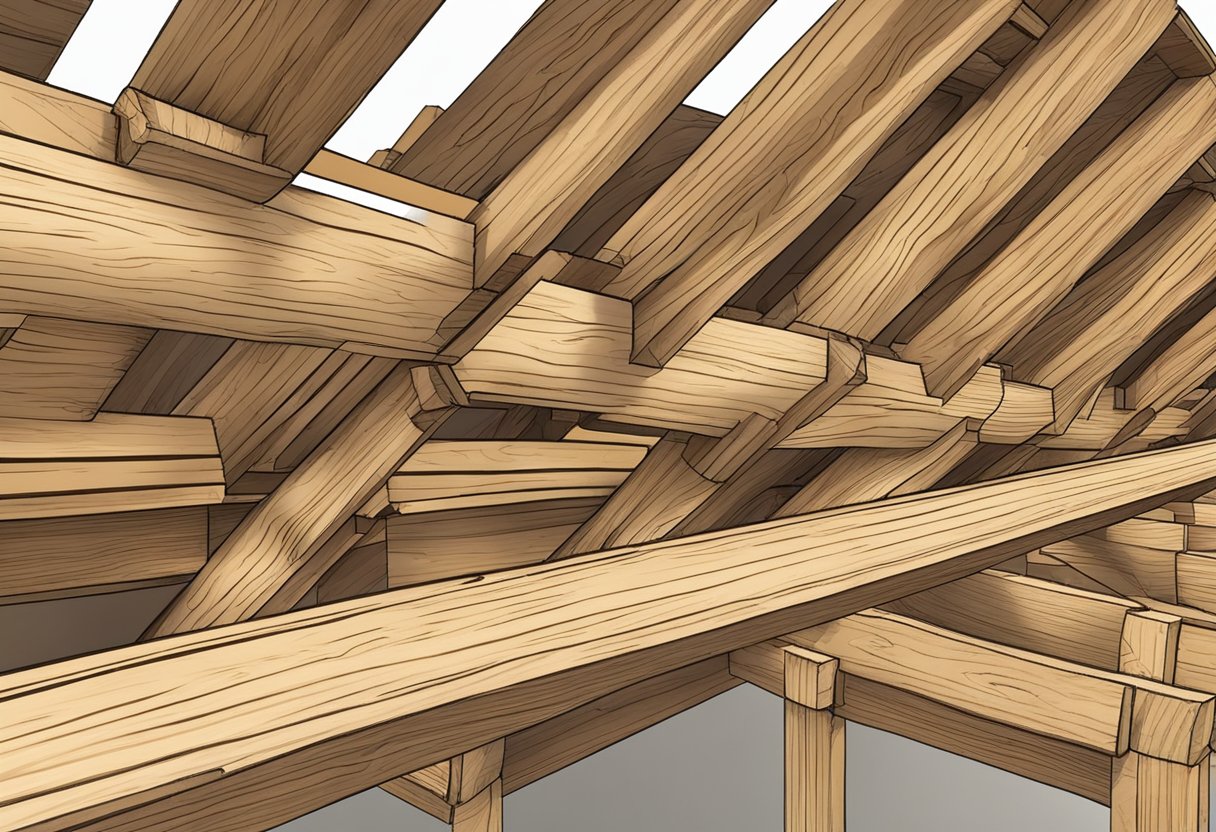
When it comes to building structures, wood beams are a popular choice due to their strength, versatility, and aesthetic appeal. There are several types of structural wood beams available, each with its own unique properties and advantages. In this section, we will explore the most common types of structural wood beams.
Solid lumber beams are made from a single piece of wood, typically a softwood like pine or fir. These beams are available in various sizes and shapes and are often used for decorative purposes like exposed ceiling beams. However, they can also provide structural support in certain applications. Solid lumber beams are easy to work with and can be cut to size on-site if necessary.
Engineered lumber beams are made from wood fibers and adhesives that are compressed and heated to create a strong, durable product. These beams are available in a variety of sizes and shapes and are often used in residential and commercial construction. Engineered lumber beams are known for their strength, stability, and resistance to warping and twisting.
Glulam beams are made by laminating several layers of wood together with adhesives to form a single, strong beam. These beams can be customized to fit specific design requirements, and are often used in large-scale commercial and industrial construction projects. Glulam beams are known for their strength, durability, and ability to span long distances without the need for additional supports.
Laminated veneer lumber (LVL) beams are made by laminating thin layers of wood veneer together with adhesives to create a strong, stable product. These beams are often used in residential and commercial construction, and are known for their strength, durability, and resistance to warping and twisting. LVL beams are available in a range of sizes and can be customized to fit specific design requirements.
In summary, there are several types of structural wood beams available, each with their own unique properties and advantages. Solid lumber, engineered lumber, glulam beams, and laminated veneer lumber are the most common types of structural wood beams used in construction today. When choosing a wood beam for your project, it is important to consider the specific design requirements and choose a beam that is strong, durable, and able to withstand the demands of the application.

Wood beams are an essential component of many structures, providing support and structural integrity. Understanding the properties of wood beams is crucial for ensuring that they are used effectively and safely. In this section, we will discuss the strength characteristics, dimensional stability, and moisture content of wood beams.
The strength of wood beams is determined by several factors, including the species of wood, the size and shape of the beam, and any defects or imperfections in the wood. The strength of wood beams is typically measured in terms of their bending strength, compression strength, and tension strength.
Bending strength is the ability of a beam to resist bending under load. Compression strength is the ability of a beam to resist compression, while tension strength is the ability of a beam to resist tension. The strength of wood beams can be improved through the use of engineered wood products, such as laminated veneer lumber (LVL) and glued laminated timber (glulam).
Wood beams are also subject to changes in dimensions due to fluctuations in temperature and humidity. The dimensional stability of wood beams is determined by the species of wood and the grain orientation of the wood fibers. For example, flat-sawn lumber is more prone to dimensional changes than quarter-sawn lumber.
The moisture content of wood beams is another important factor to consider. Wood beams with high moisture content are more prone to rot, decay, and insect infestation. On the other hand, wood beams with low moisture content are more stable and less prone to warping and cracking.
To ensure the proper moisture content of wood beams, they should be stored in a dry, well-ventilated area and protected from exposure to moisture. Moisture meters can be used to measure the moisture content of wood beams, and appropriate measures can be taken to reduce moisture content if necessary.
Overall, understanding the properties of wood beams is crucial for ensuring their safe and effective use in structural applications. By considering factors such as strength characteristics, dimensional stability, and moisture content, you can select the appropriate wood beam for your specific application and ensure its long-term performance.
When it comes to designing structural wood beams, there are several important considerations that must be taken into account. These include load-bearing capacity, beam span and size, and connection details.
The load-bearing capacity of a wood beam is determined by several factors, including the species of wood, the size of the beam, and the type of load that will be placed on it. To ensure that your beam can safely support the required load, it is important to consult with a structural engineer or other qualified professional who can help you determine the appropriate size and species of wood to use.
The span and size of your wood beam will depend on a variety of factors, including the load it will be supporting, the distance between supports, and the species of wood being used. To determine the appropriate span and size for your beam, you will need to consult with a structural engineer or other qualified professional who can help you calculate the required dimensions based on the specific requirements of your project.
The connection details for your wood beam will depend on a variety of factors, including the size and species of wood being used, the type of load that will be placed on the beam, and the specific requirements of your project. To ensure that your connections are strong and secure, it is important to consult with a structural engineer or other qualified professional who can help you determine the appropriate type of connection to use and ensure that it is installed correctly.
Overall, designing structural wood beams requires careful consideration of a variety of factors, including load-bearing capacity, beam span and size, and connection details. By working with a qualified professional and carefully considering these factors, you can ensure that your wood beam is safe, strong, and able to support the load it is designed for.
When it comes to installing structural wood beams, there are several important techniques to keep in mind. These include handling and storage, cutting and fitting, and fastening and joining. By following these techniques, you can ensure that your beams are installed safely and effectively.
Before you begin installing your beams, it’s important to properly handle and store them. Make sure that the beams are stored in a dry, well-ventilated area that is free from moisture and direct sunlight. This will help prevent warping and other damage to the wood.
When handling the beams, be sure to wear gloves and other protective gear to prevent injury. Use a forklift or other lifting equipment to move the beams, and avoid dragging them across the ground or other surfaces.
Once you have your beams in place, it’s time to start cutting and fitting them into position. Use a circular saw or other cutting tool to make precise cuts, and be sure to measure twice before cutting to ensure accuracy.
When fitting the beams, make sure that they are level and properly aligned. Use shims or other materials as needed to ensure a tight fit, and be sure to leave enough space for expansion and contraction due to changes in temperature and humidity.
Finally, it’s time to fasten and join the beams together. Use screws, nails, or other fasteners as needed to secure the beams in place, and be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper installation.
When joining multiple beams together, use a scarf joint or other appropriate technique to ensure a strong, secure connection. Avoid using butt joints or other weak connections that can compromise the structural integrity of the beams.
By following these installation techniques, you can ensure that your structural wood beams are installed safely and effectively, providing reliable support for your building or other construction project.
Maintaining and preserving structural wood beams is crucial to ensure their longevity and safety. Proper maintenance and preservation can prevent decay, insect infestation, and structural damage. In this section, we will discuss two important aspects of maintenance and preservation: Protective Treatments and Inspection and Repair.
Protective treatments are used to prevent decay, insect infestation, and other forms of deterioration. There are several types of protective treatments available, including chemical treatments, water repellents, and fire retardants.
Chemical treatments are the most common type of protective treatment used for wood beams. They involve applying a chemical preservative to the wood to prevent decay and insect infestation. The most common types of chemical preservatives used for wood beams are copper-based and include Copper Azole, Alkaline Copper Quaternary, and Copper Naphthenate.
Water repellents are used to protect wood beams from water damage. They work by creating a barrier that prevents water from penetrating the wood. Water repellents are especially important for wood beams that are exposed to the elements, such as those used in outdoor structures like bridges and decks.
Fire retardants are used to make wood beams more resistant to fire. They work by slowing down the spread of flames and reducing the amount of heat released by the wood. Fire retardants are especially important for wood beams used in commercial and industrial buildings.
Regular inspection and repair are essential to maintaining the integrity of wood beams. Inspections should be conducted at least once a year to check for signs of damage, such as cracks, splits, and decay. If any damage is found, repairs should be made immediately to prevent further damage.
Repairs may include replacing damaged sections of the wood beam or reinforcing the beam with additional support. It is important to use the correct materials and techniques when making repairs to ensure the structural integrity of the beam is not compromised.
In conclusion, proper maintenance and preservation are essential to ensuring the longevity and safety of structural wood beams. By using protective treatments and conducting regular inspections and repairs, you can extend the life of your wood beams and prevent costly damage.
1. What are chipboard loft panels? Chipboard loft panels are wooden panels made from compressed wood chips and resin. They are commonly used to create a sturdy flooring surface in loft spaces, providing support for storage and easy access to utilities.
2. How do chipboard loft panels differ from other types of loft flooring? Chipboard loft panels are lightweight yet durable, making them ideal for loft spaces. They are typically more affordable than solid wood or engineered wood flooring options, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious homeowners.
3. Are chipboard loft panels suitable for heavy loads? Chipboard loft panels have a weight-bearing capacity that makes them suitable for moderate to heavy loads, such as storage boxes, furniture, and other household items. However, it’s essential to distribute weight evenly across the panels and avoid exceeding their load-bearing limits.
4. Can chipboard loft panels be installed by homeowners? Yes, chipboard loft panels are relatively easy to install and can be done by homeowners with basic DIY skills. However, it’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully and ensure proper support for the panels to prevent sagging or structural issues.
If you are interested in any of our products or would like to discuss a customized order, Please feel free to contact us.